Starting a small business is a dream for many people around the world. The idea of being your own boss, creating something valuable, and achieving financial independence is appealing. However, while the idea sounds exciting, turning it into reality requires careful planning, dedication, and knowledge. In this article, we will explore step by step how to start a small business, covering everything from the initial idea to running your business successfully.
1. Understand Your Motivation

Before diving into the practical aspects of starting a business, it is important to understand why you want to start one. Some people want financial independence, while others are driven by passion for a particular product or service. Understanding your motivation will help you stay focused and committed, especially during challenging times.
Ask yourself questions like:
- Do I want to make money, or do I want to solve a specific problem?
- Am I ready to dedicate time and effort consistently?
- What are my long-term goals for this business?
Answering these questions honestly will help you define your purpose and guide your decisions.
2. Identify a Business Idea
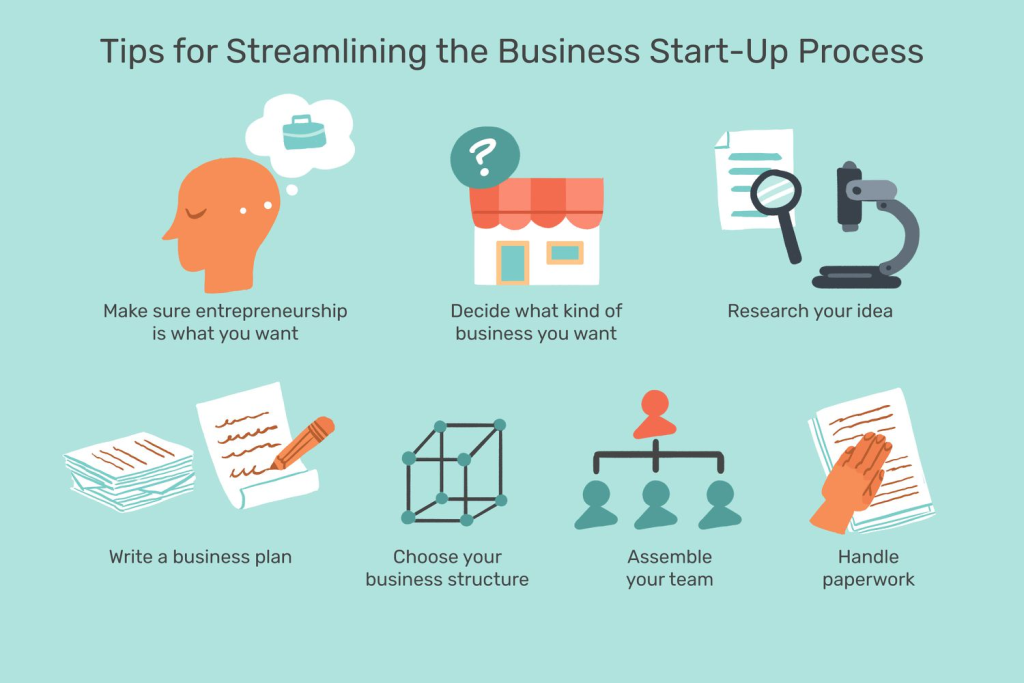
A successful business begins with a good idea. The idea should address a problem, meet a need, or offer something unique to potential customers. To identify a business idea:
- Assess your skills and interests: Choose something you are passionate about and have knowledge of. This will make running the business more enjoyable.
- Research the market: Understand what people need and what solutions are currently available. Look for gaps in the market.
- Consider profitability: Ensure there is potential to make a profit from your idea. Not every idea, even if creative, can sustain a business.
Remember, the best business ideas are often simple solutions to everyday problems.
3. Conduct Market Research
Market research is crucial for understanding your potential customers, competitors, and industry trends. This step helps you validate your idea and reduces the risk of failure.
Key steps in market research include:
- Identify your target audience: Know who will buy your product or service, their age, preferences, and buying habits.
- Study competitors: Analyze similar businesses to see what works and what doesn’t. Identify opportunities to stand out.
- Evaluate demand: Make sure there is sufficient demand for your product or service. Surveys, interviews, and online research can help.
Market research provides insights that will shape your business strategy and marketing efforts.
4. Create a Business Plan
A business plan is a roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. A well-thought-out business plan increases your chances of success and is often required if you seek funding.
A typical business plan includes:
- Executive summary: An overview of your business and goals.
- Business description: Details about your product, service, and target market.
- Marketing plan: How you plan to attract and retain customers.
- Operational plan: How the business will function daily, including suppliers and staffing.
- Financial plan: Budget, pricing, projected income, and expenses.
Even if you do not intend to get investors, writing a business plan helps you clarify your vision and strategy.
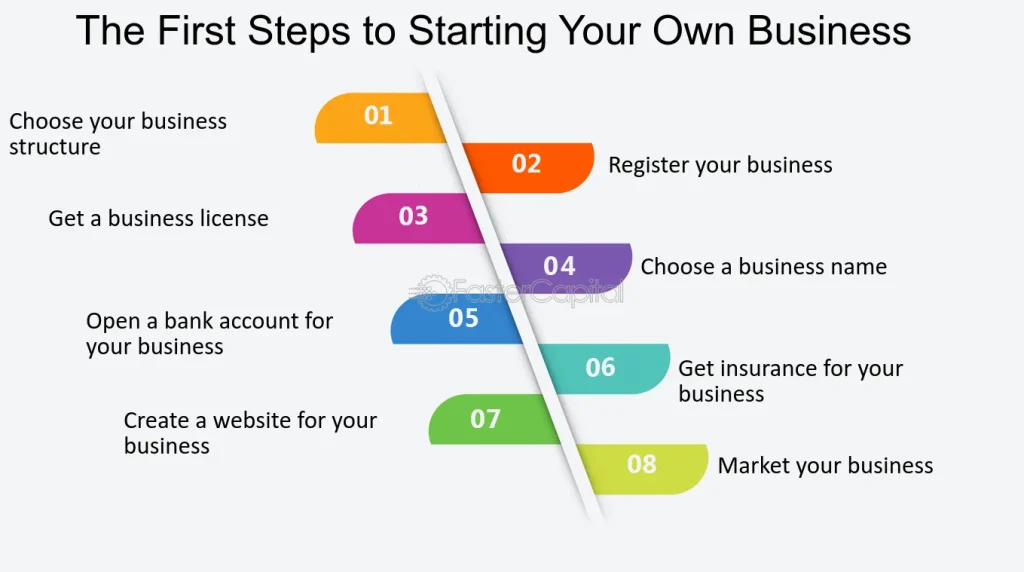
5. Choose a Business Structure
Your business structure affects legal responsibilities, taxes, and personal liability. Common small business structures include:
- Sole proprietorship: Simple to set up, but the owner is personally liable for debts.
- Partnership: Shared ownership with partners, sharing profits and responsibilities.
- Limited liability company (LLC): Offers personal liability protection while maintaining flexibility.
- Corporation: More complex structure with legal protection and opportunities for growth.
Choose a structure that fits your business size, goals, and risk tolerance.
6. Register Your Business
Once you choose a structure, register your business with the relevant government authorities. This process may involve:
- Registering your business name.
- Obtaining a tax identification number.
- Securing necessary licenses and permits based on your industry.
Proper registration ensures your business operates legally and builds credibility with customers.
7. Secure Funding
Starting a business requires money for initial setup, equipment, inventory, and operations. Depending on your business type, funding options may include:
- Personal savings: Using your own funds reduces debt but carries personal risk.
- Family and friends: Borrowing from trusted sources.
- Bank loans: Traditional business loans may require collateral and a business plan.
- Investors: Offering equity to investors in exchange for capital.
- Government grants or programs: Some countries provide support for small businesses.
Careful planning of finances ensures that your business can survive its early stages without running into cash flow problems.
8. Set Up Your Business Location
Depending on the type of business, you may need a physical location, office space, or simply an online presence. Consider:
- Accessibility for customers.
- Cost of rent or purchase.
- Utility and operational needs.
- Online presence and website development for digital businesses.
The right location or platform can significantly impact your business’s success and customer reach.
9. Develop Your Brand
Branding is more than just a logo. It reflects your business identity, values, and how customers perceive you. Strong branding helps you stand out and build trust.
Key elements of branding include:
- Business name: Memorable and relevant.
- Logo and design: Visual representation of your business.
- Message and tone: How you communicate with customers.
- Customer experience: Consistent quality and service.
Invest time in building a brand that resonates with your target audience.
10. Market Your Business
Marketing is essential to attract customers and grow your business. Depending on your audience and budget, marketing strategies can include:
- Social media promotion.
- Content creation such as blogs or videos.
- Email campaigns and newsletters.
- Local advertising and word-of-mouth referrals.
- Attending trade shows or events.
The key is to reach the right people with the right message, consistently.
11. Launch Your Business
After thorough preparation, it’s time to launch. A launch strategy can include:
- Hosting a small launch event.
- Offering special promotions or discounts.
- Announcing your business through social media and press releases.
- Collecting initial customer feedback to refine products or services.
A successful launch sets the tone for your business’s early growth.
12. Manage Operations and Finances
Once your business is running, daily operations and finances require constant attention. Keep track of:
- Revenue and expenses.
- Inventory and supply chain.
- Employee management and productivity.
- Customer satisfaction and feedback.
Efficient management ensures smooth operations and long-term profitability.
13. Adapt and Grow
No business remains the same forever. To stay competitive:
- Continuously evaluate market trends and customer needs.
- Innovate your products or services.
- Expand to new markets or platforms.
- Learn from mistakes and adapt quickly.
Flexibility and a willingness to evolve are key traits of successful entrepreneurs.
Conclusion
Starting a small business is a challenging but rewarding journey. From understanding your motivation to managing operations and growing your business, every step requires careful planning and dedication. By following these steps, you can increase your chances of building a sustainable and successful business. Remember, success does not happen overnight, but persistence, creativity, and hard work can turn your small business dream into reality.